
Shunt resistors are usually associated a parallel position along with an instrument or the component. This is done to divert an electrical current. These types of resistors provide alternative current paths in case there have been problems or failure and these are used for complete reduction of input sensitivity from the input lines through the ground.Current shunt resistors were generally low in resistance and passive electronic devices used to measure AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) going through the voltage drop in which currents created throughout resistance.
The electrical specifications of the shunt resistors involve resistance tolerance, power rating, resistance power coefficient, resistance temperature coefficient, ohms, and current rating. Ohms measure the material opposition into an electric flow of circuit while temperature coefficient of resistance (or TCR) refers to the change in resistance along with change in temperature.
PCR or the power coefficient of resistance is referring to a temperature. This temperature rises because of self-heating. For the current-sensing shunts, the resistance usually ranges from 100 µO up to 500 mO. A shunt resistor can be applied in current conversion. This is the aspect in which high precision has been required.
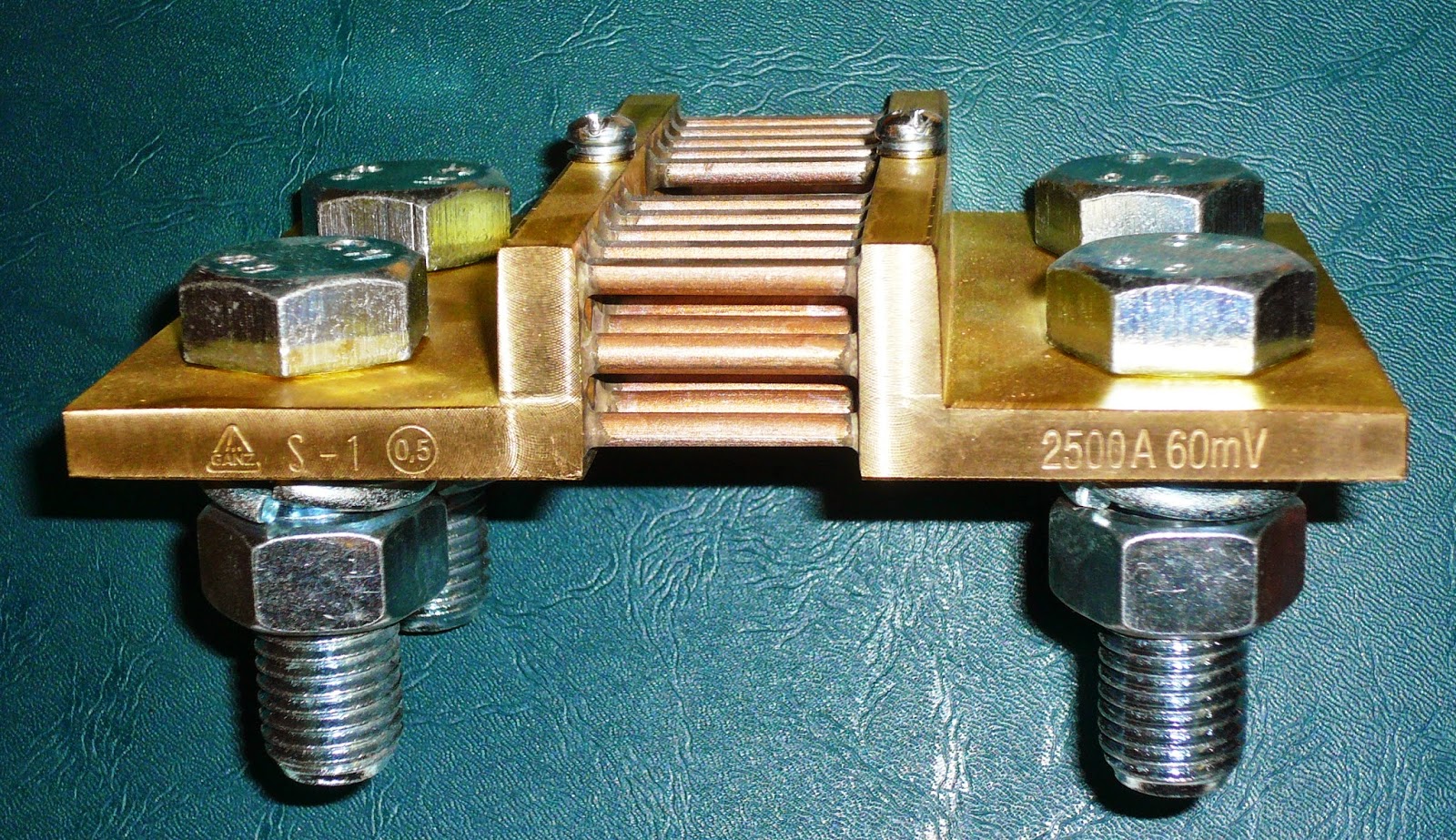
The physical specifications for the shunt resistors involve resistor materials and lead type. A shunt resistor can be surface mounted, chassis mounted, through-hole mounted, and bolted. THT or the through-hole technology and SMT or the surface mount technology are both other popular and common mounting styles. The other kinds of lead are screw terminals, J-leads, and tab terminals. There are also gull-wing leads, radial leads, and axial leads available.
Shunt resistors without leads are also available and they can be wire wound, metal film, metal oxide, carbon film, ceramic, metal alloy, thin film, and thick film. The carbon shunt resistor has been comprised of high temperature, resistive, solid and ceramic materials that have been bonded by the metal contacts.
Metal allow shunt resistors have 2 or more elements while a wirewound shunt resistor has thin wire winding in a ceramic rod. Each shunt resistor becomes unique in the area of packing because of passive electronic components that were packed in tape reel assemblies. This includes carrier tape which had embossed cavities for individual component storage. Others have been packed in trays (or trails) and they had been made up of carbon-power and fiber materials as they molded in rectangular outlines containing uniformly spaced matrices of pockets. Some of them have been packed in a tray (trail) and were comprised of both fiber and carbon-power materials. At the same time, these are molded in a rectangular form that has numerous pockets which were uniformly spaced.
No comments:
Post a Comment